
Updated on 28/11/2024
Most workplaces are quite noisy. Sometimes the sound volume can be so high that the noise level exceeds the limit of 130 dB, which is almost as loud as a plane taking off. Hence the importance of knowing where and when to wear hearing protection, which hearing protection would be most suitable, and what the consequences may be if you do not wear hearing protection.
Choosing from all the different types can be difficult. Especially since protective values can vary greatly depending on the environment, the source and duration of the noise, and even the type of protective equipment you use.
We are here to help you get started.
In this blog post, you'll learn all about hearing protection.
- Why is it necessary to wear hearing protection?
- At what point is your hearing damaged?
- When should hearing protection be worn (limits and health supervision)?
- Decibel values
- Standards en marking
- Dempingswaarden
- Attenuation levels
- Kies de juiste dempingsgraad
- Analyseer het geluid
- Selecteer het meest geschikte type gehoorbescherming
- Correct use
- Life expectancy and maintenance
Why wear hearing protection?
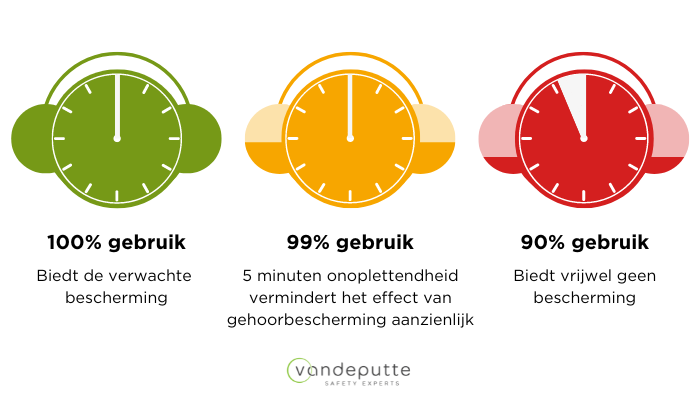
Damage to your hearing caused by loud noises can happen quicker than you think. Many people think that they can work next to a noisy machine without hearing protection, or they can remove the hearing protection for five minutes if they’ve been wearing it all day long. However, the decrease in protection against hearing damage happens far quicker than you think:
- 100% use of hearing protection provides the level of expected protection
- 99% of use (about 5 minutes less) already reduces the effective level of the protection
- 90% of use provides no protection at all
This means that, by not wearing hearing protection for even a very short period of time, the risk of irreversible hearing damage is increased significantly.
At what point is your hearing damaged?
Hearing damage occurs when the tiny stereocilia cells in the inner ear are damaged. This damage is permanent, affecting the rest of your life.
There are a number of symptoms you’ll experience if you’ve suffered hearing damage. The best known examples are a continuous ringing sound (tinnitus) and hissing. However, if you can no longer hear high-pitched or quiet sounds, there’s a chance that your hearing is damaged. Or if you have difficulties when making a phone call or holding a conversation in a noisy environment.
In addition to these hearing impairments, you may also experience certain medical issues as a result of hearing damage:
- Disturbed sleep
- Loss of concentration
- Tiredness
- Headaches
- High blood pressure
What can you do to protect your ears? Simple: wear hearing protection.
In a noisy environment, wearing hearing protection is essential to prevent hearing damage.
When should hearing protection be worn?
Hearing protection is governed by European Directive 2003/10/EC, which specifies when hearing protection must be worn.
The directive is based on three limits for daily exposure to noise: 80, 85 and 87 decibels (dB).

| Limit value | Measures | Health monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| 80 dB(A) |
|
Every 5 years |
| 85 dB(A) |
|
Every 3 years |
| 87 dB(A) |
|
Every year |
Health monitoring
During the mandatory health audits, the Committee for prevention and protection at work (CPBW) will assess the risks, the measures taken to reduce the noise risks, and the selected hearing protection.
The table above shows how often health monitoring is required.
Period of exposure
To prevent hearing damage, employees must not work for prolonged periods in noisy environments.
The acceptable time period depends on the sound pressure (dB(A). This table shows the maximum exposure to noise at different sound pressure levels.
| Sound pressure in dB(A) | Maximum exposure |
|---|---|
| 80 dB(A) | 8 hours |
| 83 dB(A) | 4 hours |
| 86 dB(A) | 2 hours |
| 89 dB(A) | 1 hour |
| 92 dB(A) | 30 minutes |
| 95 dB(A) | 15 minutes |
| 98 dB(A) | 7 minutes |
| 101 dB(A) | 3 minutes |
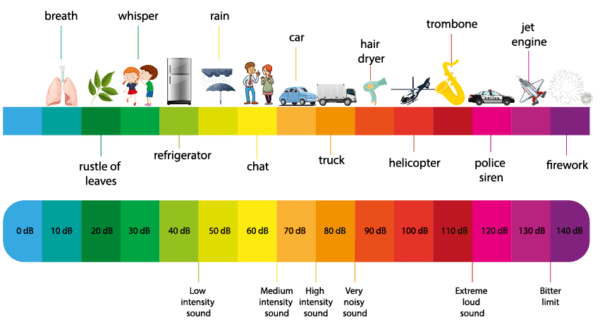
Decibel values
How loud is 80 dB?
The noise level of a gentle conversation or a quiet street is around 40 dB. An ordinary conversation is around 60 dB, and a busy motorway is about 80 dB. The noise level of live music is approximately 90 dB. Our pain threshold lies at 120 dB.
Standards and marking
According to the European Directive, hearing protection must comply with the EN 352 standard.
This includes information, definitions and testing methods, and covers the effectiveness of hearing protection equipment. Each item of hearing protection has its own code:
- EN 352 - 1: Ear muffs
- EN 352 - 2: Earplugs
- EN 352 - 3: Ear muffs attached to industrial safety helmets
- EN 352 - 4: Level-dependent ear muffs
- EN 352 - 5: Active noise reduction (ANR) ear muffs
- EN 352 - 6: Ear muffs with safety-related audio input
- EN 352 - 7: Level-dependent earplugs
There is no marking on earplugs This can be found on the smallest packaging component (bag or box).
Marking is highly brand-dependent for reusable earplugs and otoplastics. Some brands use colours to indicate the type of filter and/or which hearing protection unit is inserted in the left or right ear.
With ear muffs, some markings are consistently indicated, i.e.
- Brand name and company logo
- Article name
- CE approval mark
- The EN standard (EN 352)

Attenuation levels
Hearing protection devices have an attenuation level that indicates by how many decibels the noise level is reduced on average. This will help to select the appropriate type of hearing protection.
This value is indicated in 3 ways:
SNR value (Single Number Rating)
The SNR value is one average attenuation value for all frequencies.
An SNR value of 35 dB, for example, indicates that a noise level of 100 dB will be reduced to 65 dB. This figure is a good way of comparing different audio protection devices.
In most circumstances, machines produce noise within specific frequencies. To make a final choice, we recommend being guided by the HML values and frequencies.
HML value (high, medium and low frequencies)
The HML value determines the frequencies (high, medium and low) in all three groups of frequency, and is therefore more accurate than SNR values.
- H = between 2000 and 8000 Hz
- M = between 1000 and 2000 Hz
- L = between 63 and 1000 Hz
Octave band analysis
This is the most accurate method, because octave band analysis measures the noise level at a greater range of frequencies (63, 125, 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 and 8000 Hz).
SNR, HML and octave bands are all stated on the packaging.

How to choose the most suitable hearing protection?
You can't simply say that one ear protection device is better than another, as it all depends on the attenuation levels. The best ear protection is the device that:
- Protects you correctly
- Is sufficiently comfortable to be worn for a full working day
- Allows you to remain in contact with your environment
Step 1: Analyse the noise level in the workplace
Qualitative sound measurement is the basis for effective hearing protection and correct noise filtration selection.
Good sound measurement includes:
- Measuring all relevant situations
- Latest information (sound measurements must be recent and be representative of the current workplace and situation)
- Clarity regarding the exposure time of employees
- Frequency-specific information
- Inadequate sound measurement can lead to insufficient or excessive attenuation, which may compromise both hearing and workplace safety.
Be sure to read: The importance of high quality sound measurement
Step 2: Determine the appropriate protection for each situation
When choosing ear protection, it is important to take various factors into account:
- Attenuation & protection: Choose ear protection with the correct attenuation to match the noise levels to which the wearer will be exposed. Sufficient attenuation without being over-protected. Over-attenuation results in inadequate awareness of speech, environmental and warning sounds which, in turn, increases the risk of accidents. This may lead to the hearing protection equipment being worn less frequently, thereby reducing the overall level of protection.
- Use in combination with other PPE: Make sure that the ear protection is compatible with other PPE that must be worn, and that, when combined, they comply with the requirements of the relevant directives.
- Fit check: Make sure that the ear protection fits properly in order to provide the best protection. (refer to article on Face-Fit tests)
- Comfort & ergonomics: Choose ear protection that is comfortable, otherwise you may want to avoid wearing it.
- Situational awareness & communication: Consider how important it is to be able to hear ambient sounds. If this is important, you should choose active hearing protection.
Did you know that: 40% of employees choose the wrong type of ear protection and/or wear it incorrectly?* This is according to the HSE study report RR720 ‘Real world use and performance of hearing protection’.
Step 3: Select the most suitable type of hearing protection.
Once you know the noise levels you are exposed to on a daily basis, you can continue to choose the correct type of hearing protection for your work.
There are different types of hearing protection. From simple, inexpensive earplugs to hearing protection that is customised to fit an individual wearer. What you need will depend on your workplace situation and the application.
Earplugs
Earplugs are available in different shapes and attenuation values: Disposable, reusable, push-to-fit and banded earplugs. Most earplugs are made from a type of foam. These earplugs are usually disposable products, are inexpensive and maintenance free.
There are also silicone earplugs that can be washed and reused. These are more environmentally friendly, but they need to be well maintained.
Shape and durability are important when choosing earplugs. These properties determine whether the earplug can be easily inserted into the ear canal and will remain in place.
If you need to regularly insert and remove your earplugs, then those equipped with a cord or ear-loop are the best choice. The cord prevents the earplugs from falling out.
In some companies (often in food companies), it is even more important to be able to retrieve an earplug quickly if it has fallen out. Metal detectable earplugs are available for this purpose. These are usually blue in colour and have small amounts of metal in both the earplug and the cord.
| Benefits of earplugs | Disadvantages of earplugs |
|---|---|
|
Good attenuation over a large frequency range Comfortable, with no pressure on your ears Maintenance-free |
Sometimes difficult to insert Expensive if the disposable type is used |


Ear muffs
Apart from earplugs, you can also wear ear muffs to prevent hearing damage. There are a number of types available:
Level-dependent ear muffs
- Passive ear muffs reduce the noise due to the material they’re constructed from. The level of hearing protection depends on the sound level. Passive ear muffs are effective against high-pitched sounds, such as alarms.
- Active ear muffs have a built-in electronic system. This system detects a low noise through a microphone, and amplifies and transmits it to a loudspeaker in the earcup, and vice versa. This helps to control the sound in the ear muff.
With external audio input
- Radio ear muffs or ear muffs with a connection for a smartphone and Bluetooth dampen ambient noise, however the wearer can still receive signals, music and other messages.
- Nowadays, many ear muffs use DAB+, which delivers digital sound quality.
- Communication ear muffs also have a walkie-talkie or GSM. This allows employees to communicate more easily without the need to remove their hearing protection.
See all ear muffs with Bluetooth
See all communication ear muffs

Ear muffs can almost always be used and are extremely effective at very high sound pressure levels. If you need to frequently switch between wearing and removing your hearing protection, ear muffs are a better choice than earplugs.
Helmet-mounted ear muffs are easily attached to an industrial safety helmet. This usually involves an adapter but varies per brand. They are available as passive, active or communication ear muffs.
See all helmet-mounted ear muffs

| Benefits of ear muffs | Disadvantages of ear muffs |
|---|---|
|
Ear muffs fit everyone Ear muffs provide effective noise attenuation Reliable attenuation data available Communication is maintained |
Sometimes uncomfortable due to pressure during prolonged use Uncomfortable in warm and humid environments Difficult to work with in confined spaces If used intensively, ear pads should be regularly replaced or cleaned Communication ear muffs especially are expensive |
Otoplastics
Otoplastics are earplugs that are tailor-made according to an impression of the wearer's ear canal. As a result, they are extremely comfortable.
Filters can be included, which ensure correct noise attenuation in specific working environments. They also enable effective communication with other people.
In most cases, the level of acceptance among employees is very high when otoplastics have been selected. Furthermore, you pay a fixed price per user. So, you know what your costs will be.

| Benefits of otoplastics | Disadvantages of otoplastics |
|---|---|
|
Otoplastics have a long lifespan and are therefore very economical in the long term Otoplastics are discreet during use They are easy to insert They fit very well and are comfortable |
High purchase price Cannot be purchased off-the-shelf; must be made to measure |
| Hearing protection | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Disposable earplugs |
|
|
| Reusable earplugs and banded earplugs |
|
|
| Passive earmuffs |
|
|
| Active noise-reduction earmuffs |
|
|
| Communication earmuffs |
|
|
| Otoplastics |
|
|
Correct use
Providing information on the importance of hearing protection
Organising informational sessions and toolbox meetings is essential in order to emphasise the importance of hearing protection. These meetings explain why hearing protection is crucial, and what the consequences are of not wearing hearing protection, even for short periods of time.
The correct way to wear hearing protection?
To ensure that your hearing is well protected, you must insert earplugs correctly. If this is not done correctly, your hearing could still be damaged. Watch our 'how to' video for help on how to do this.
It is also important to use signage with pictograms to indicate which hearing protection must be worn and where. In some companies, both their workplaces and their corresponding hearing protection are colour coded (green, yellow, orange, red). This tells employees exactly which type of hearing protection must be worn where.
Motivating employees to wear hearing protection most effectively?
It is essential to motivate employees and raise their awareness regarding the importance of wearing the correct hearing protection. This can be achieved through motivation campaigns and informative toolbox sessions.
In addition, creating a culture of engagement is of great importance. When you find that a colleague is not wearing their hearing protection, or is not using it correctly, it is important to discuss this with them.
Lifespan and maintenance
Earplugs
Earplugs generally last for just one working day. Disposable earplugs must be replaced more frequently than reusable earplugs. Once they have been used, they do not need to be maintained and are disposed of in the waste bin.
Reusable earplugs and banded earplugs are cleaned with warm water and soap or a disinfectant cleaning product. Then dried with a soft cloth.
Ear muffs
Ear muffs last somewhat longer. Change the ear pads regularly so that the attenuation level remains consistent. Most brands provide hygiene sets so that pads can be replaced regularly. We recommend you do so twice per year.
If you use communication ear muffs, don't forget to replace the microphone too.
Otoplastics
Want to use comfortable, long-term hearing protection? Then choose otoplastics. Thanks to the personalised characteristics and an annual leak test, they offer comfortable ear protection for a considerable time.
Just like earplugs, otoplastics can be cleaned using soap and water. Or by using the supplied cleaning product and cloth.
Would you like expert advice?
You can come to Vandeputte not only for advice, but we can also carry out qualitative sound measurements for you.


